Mealy Machine Verilog Code | Moore Machine Verilog Code
- Bcd Adder Verilog
- Half Adder Verilog Code
- 3 Bit Adder Verilog Code
- 1 Bit Full Adder Verilog
- 4 Bit Ripple Adder Verilog
- Full Adder Verilog Code
Design will be a serial adder. It will take 8-little bit inputs A and T and adds them in a serial fashion when the goinput is certainly fixed to 1. The outcome of the operation is kept in a 9-little bit sum sign up, The engine block diagram is attached. I was using Quartus II 13.0sg1 (64-bit) Internet Model. Fig: State table for the Mealy type serial adder FSM Fig: State-assigned table for the Mealy type serial adder FSM Fig: Circuit for Mealy type serial adder FSM. The flip-flop can be cleared by the Reset signal at the start of the addition operation. Moore type FSM for serial adder: In a Moore type FSM, output depends only on the present state.
This page covers Mealy Machine Verilog Code andMoore Machine Verilog Code.
Mealy Machine Verilog code
Following is the figure and verilog code of Mealy Machine.
Bcd Adder Verilog
output out;
input in;
input clk, rst;
reg out;
reg[1:0] state;
parameters0=2'd0, s1=2'd1, s2=2'd2, s3=2'd3;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(rst0) begin state=s0; out=0; end
else begin
case (state)
s0: if(in0) begin out=0; state=s1; end
else begin out=0; state=s0; end
s1: if(in0) beginout=0; state=s1; end
else begin out=0; state=s2; end
s2: if(in0) begin out=0; state=s3; end
else begin out=0; state=s0; end
s3: if(in0) begin out=0; state=s1; end
else begin out=1; state=s2; end
default: state=s0;
endcase
end
endmodule
Moore Machine Verilog code
Following is the figure and verilog code of Moore Machine.
output out;
input in;
input clk, rst;
reg out;
reg[1:0] state;
parameter s0=2'd0, s1=2'd1, s2=2'd2, s3=2'd3;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(rst0) begin state=s0; out=0; end
else begin
case (state)
s0: begin out=0; if(in0) state=s1; else state=s0; end
s1: begin out=0; if(in0) state=s1; else state=s2; end
s2: begin out=0; if(in0) state=s3; else state=s0; end
s3: begin out=1; if(in0) state=s1; else state=s2; end
default: state=s0;
endcase
end
endmodule
Verilog source codes
Low Pass FIR Filter
Asynchronous FIFO design with verilog code
D FF without reset
D FF synchronous reset
1 bit 4 bit comparator
All Logic Gates
RF and Wireless tutorials
Share this page
Translate this page
The serial adder is a digital circuit in which bits are added a pair at a time.
Let A and B be two unsigned numbers to be added to produce Sum = A + B. In this we are using three shift registers which are used to hold A, B and Sum. Now in each clock cycle, a pair of bits is added by the adder FSM and at the end of the cycle, the resulting sum is shifted into the Sum register.
Half Adder Verilog Code
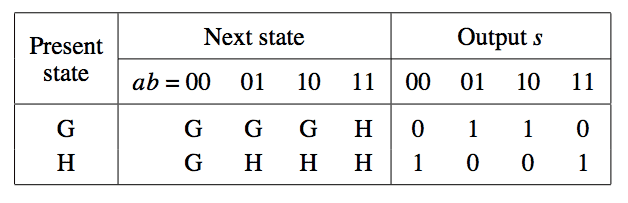
Mealy type FSM for serial adder:
Let G and H denote the states where the carry-in-values are 0 and 1. Output value s depends on both the state and the present value of inputs a and b.
In state G and H:
| Input valuation | Output (s) | State |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0 | FSM will remain in same state G |
| 01,10 | 1 | FSM will remain in same state G |
| 11 | 0 | FSM moves to state H |
| 01,10 | 0 | FSM will remain in same state H |
| 11 | 1 | FSM will remain in same state H |
| 00 | 1 | FSM moves to state G |
3 Bit Adder Verilog Code
A single Flip-Flop is needed to represent the two states. The next state and output equations are:
Y = ab + ay + by
1 Bit Full Adder Verilog
s = a ⊕ b ⊕ y
The flip-flop can be cleared by the Reset signal at the start of the addition operation.
4 Bit Ripple Adder Verilog
Moore type FSM for serial adder:
In a Moore type FSM, output depends only on the present state. Since in both states, G and H, it is possible to produce two different outputs depending on the valuations of the inputs a and b, a Moore type FSM will need more than two states. Therefore we will four states namely: G0, G1, H0 and H1.
The next state and output equations are:
Y1 = a ⊕ b ⊕ y2
Y2 = ab + by2 + by2
s = y1
The only difference between circuits of Mealy and Moore type FSM for serial adder is that in Moore type FSM circuit, output signal s is passed through an extra flip-flop and thus delayed by one clock cycle with respect to the Mealy type FSM circuit.
Full Adder Verilog Code
References: Fundamentals of Digital Logic with VHDL Design